A First Project for the Boolean Board#
Learning Goals#
know the basic definitions of voltage, current, ohms law
design tools and technologies
(how to install the design tool)
know how to write a basic circuit description in Verilog
know how to connect general purpose IO (GPIO)
programming or configuring an FPGA
Introduction#
Exercise 2
What is the difference between a
programming language
hardware description language ?
Solution to Exercise 2
A programming language is used to write software for a processor which is compiled to a binary. A hardware description language in short HDL is in contrast used to describe hardware, for example a processor or memory. A HDL can be synthesized to logic gates and then converted to a software which is not run but used to configure an FPGA.
Exercise 3
You probably heard the terms
programming an FPGA
configuring an FPGA
What is the difference?
Solution to Exercise 3
From the Introduction to FPGA Design for Embedded Systems Course – Coursera:
Programming usually describes the action of placing into memory the contents of a file that will be used to define the behavior of the device, whether it be a microcontroller or a programmable logic device. Configuration is the process of loading that memory into the device to establish the characteristic behavior.
Exercise 4
What are the typical design steps for developing a circuit for an FPGA?
Solution to Exercise 4
setting up design specifications, i.e., what should the product deliver?
writing/discussing implementation details using, e.g., state diagrams, behavioral diagrams, text etc. Mostly required in complex designs.
writing code
verification of the design using simulation
synthesis, mapping, routing, creating bitstream (binary which gets programmed into a memory chip to configure the FPGA)
(post-synthesis, -map, -route verification in rare cases)
testing the design on the hardware
Background#
A First Look at Circuits#
Exercise 5
What does a typical circuit consist of?
Solution to Exercise 5
power supply (potential chemical energy)
switch (for cutting the circuit)
load (where the energy is used)
Exercise 6
The height of water stored in an elevated container gives the water a potential energy. Which of the following is the equivalent of this energy in electricity?
A) voltage B) current C) charge D) wire E) I don’t know
Solution to Exercise 6
Voltage.
The movement of the electrons on the conductor would be similar to the kinetic energy of the water released from the elevated container.
This energy in turn is converted to heat, light, motion in a load.
Exercise 7
How much current does a small LED like on the Boolean board typically draw (in terms of range)?
A) μA B) mA C) A D) kA E) I don’t know
Solution to Exercise 7
mA
For example look into the datasheet of a blue 0805 LED
Exercise 8
Which value should the resistor have if we connect this 0805 LED to a 5V supply?
Solution to Exercise 8
According to the datasheet the LED has typical forward voltage of 3.3 V at 20 mA. To achieve this, we need a resistor which is loaded with the rest of the voltage 1.7V. \(I × R = V\) Thus:
\( 1.7 V / 20 mA = 85 Ω \)
Signals#
Attention
The following figure from RealDigital seem to be erroneous:
The author calls everything between the load components signals, but how do these components draw power?
The wires that carry power supply are called rail wires. Power Rail is the voltage source. Signals are for information exchange.
There is a similarity to the railway transportation system, where rails can be used for electrification. Railways require also signalling
Exercise 9
An embedded module has typically a power supply interface and a communication interface based on a serial interface. Do you know an interface which can deliver both power and information?
Solution to Exercise 9
Electric Vs. Electronic Circuits#
Exercise 10
What is the difference between
electric and electrical?
electric and electronic?
Is an electronic device also an electrical device?
Solution to Exercise 10
According to Wiktionary electrical is a synonym of electric
According to Wiktionary, electronic is:
Operating on the physical behavior of electrons, especially in semiconductors
Electronic devices, in short electronics uses active devices to control the flow of electrons, compared to passive components like resistors, capacitors and inductors.
Another interesting thought from Stackexchange:
… Because electronic devices are typically used for representing and manipulating information, this makes for a simple rule of thumb for distinguishing electrical and electronic. …
Yes. An electronic device uses electrical infrastructure and properties, but an electrical device does not have to use electronic properties typically found in semiconductors.
Exercise 11
Why are communication and information processing devices typically integrate more digital modules/components than analog?
Solution to Exercise 11
According to the Wikipedia article – Analogue vs digital electronics there are more manpower and efficient tools to design digital systems. To my understanding, they have both their pros and cons regarding precision and noise. Precision of a digital systems is dependent on the quality of analog-digital converters. The quality of an analogue signal will degrade continuously with an increasing noise (remember analogue walkie-talkies). In contrast, a digital signal fails abruptly if the noise is too high. A human can still understand an analogue signal despite high noise, but a digital computer program may want to throw a signal away if only a part of it cannot be decoded due to high noise.
Finally note that the modern digital computers are not efficient at solving some problems. Analog computers were used for complex simulations. Nowadays there is still research to fusion the advantages of digital and analog computing. See this educational analog computer.
Exercise 12
Do you know any communication technologies which use/used analog signals?
Exercise 13
You want to communicate a number ranging from 0 to 200 between two components. How many wires do you at least need if you communicate it using
analog signaling?
digital signaling?
Solution to Exercise 13
Using analog signaling we need only one wire. The transmitter requires a DAC (digital-to-analog converter) and the receiver an ADC (a-to-d converter).
In case of digital signaling we need minimum eight wires because we can represent 201 numbers using at least 8 bits.
Exercise 14
You have a digital system with 5V power supply voltage. How are the binary values 1 and 0 represented on the wires of such a system?
Solution to Exercise 14
There is no single rule:
If a signal is active-high, then a logical high level means
1. In other words, it is active when the logical level is high.If a signal is active-low, then a logical low level means
1.
The voltage thresholds for the logical levels depend on the technology used.
More info: Logic level – Wikipedia
Electric Charges, Voltage, Current#
Voltage#
Exercise 15
What are the voltages that you can encounter on the Boolean board?
Are these dangerous for a human?
Solution to Exercise 15
According to the schematics of the Boolean board page 14, the board is supplied with USB power, which is driven typically with 5V. The power regulator chip TPS65261RHBR converts it to 1V, 1.8V and 3.3V.
According to IEC publication 60479-1, currents up to 30 mA should not have any irreversible effects:
According to Body Resistance – Wikipedia the human body resistance can vary between 100kΩ and 500Ω dependent on the voltage and environmental conditions. In the very unlikely case of 500Ω, the current will be \(5V / 500Ω = 10 mA\)
Current#
Exercise 16
Imagine that you are connect the positive the negative poles of a battery using a cable. This will typically heat the battery even there is no resistor in series with the conductor. Why does this happen?
Solution to Exercise 16
The battery and even the conductor have a low amount of resistance. The current flowing through the battery will release the energy \(I^2 \cdot R\) as heat.
Resistance & Ohm’s Law#
Ohm’s Law#
Exercise 17
What is the Ohm’s law triangle good for and how does it work?
Solution to Exercise 17
It is a graphical representation to ease memorizing the equation.
It works as follows:
Resistance#
Exercise 18
How much is the power dissipated on the series resistor connected to a single mono-colored LED on the board?
Solution to Exercise 18
To calculate the power, we need to find out two of either the voltage, current or resistor.
The mono-color LEDs and the series resistors can be found on page 5 of the schematic. Its resistance is 330Ω. So we need to find out the current or the voltage on the resistor. One possible way is to know how much the voltage on the FPGA pin is when the pin is active.
The FPGA pins can be configured to operate at different voltages. The pins of the FPGA are organized in banks and the pins in a bank share the same voltage supply. For example the LED signal LD0 is connected to BANK35 which can be seen on page 12 of the schematic. BANK35 in turn is supplied with VCCp3V3 – you can see that on page 13: VCCO_35 connected to VCCp3V3. 3V3 stands for 3.3V.
If we look into the datasheet of a 0805 green LED, we see that the typical forward voltage is 2.1V at 20 mA. We do not exactly know the real current is, still we can approximate using these values.
If we assume that the voltage on the LED is 2.1V, then the voltage on the resistor is \(3.3V - 2.1V = 1.2V\), and the current would be \(1.2V / 330Ω ~= 4mA\)
4 mA is much less than the typical current of 20 mA. Probably we the forward voltage on the LED is lower, so the voltage on the resistor is higher and thus the current will be a bit higher than 4 mA.
If we look at the forward current vs forward voltage plot at page 3 of the LED datasheet. Then we see a forward voltage of roughly 1.9V at 5mA. Using these values we can calculate the power \(P = I^2 \cdot R = (5mA)^2 \cdot 330Ω ~= 8mW\).
A more precise approach would be to measure the actual voltage using a multimeter, as the LED used on the board may have different specifications.
TODO
You may have discovered in the board constraint file (XDC)[1] that the LED pin is configured as LVCMOS33 which is signaling standard like LVDS. LVCMOS is actually a semiconductor technology like TTL, but the same naming is also used for the switching standard for (information) signals.
DC Input and Output Levels – Spartan-7 datasheet states:
Footnote 5: Supported drive strengths of 4, 8, 12, or 16 mA in HR I/O banks.
It looks like the pin is actually a current source. For more info look to this thread in EEVBlog. So we need to search for the default drive strength setting.
TODO
Electronic Components#
Resistors#
You can see several rectangular white boxes with RN on the Real Digital board silk-screen
This is not true for the resistors on the front side of the Boolean board. The resistors on the rear side are named.
Capacitors#
Exercise 19
What are the capacitors very close to the FPGA good for?
Why are there different sizes?
Solution to Exercise 19
These are decoupling capacitors. These are used to alleviate the sudden energy needs of the chip which could cause voltage dips (a.k.a brownout) by acting as a close charge reserve.
Typically there are different sizes which are placed in parallel. Each capacitor is optimal for filtering the dips at a specific frequency range – small capacitors tend to response better at higher frequencies:
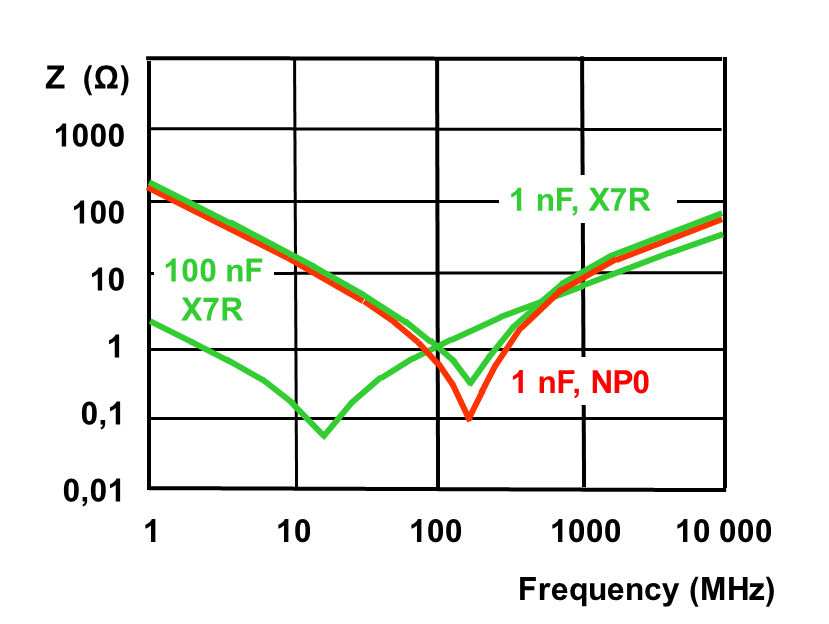 .
.
We see that the 1nF, NP0 capacitor has a lower impedance at about 300 MHz compared to other capacitors, thus can deliver the charge faster to the circuit.
More info: Decoupling capacitor – Placement:
A transient load decoupling capacitor is placed as close as possible to the device requiring the decoupled signal.
Physical vs Model Circuits#
Physical Circuits#
Physical circuits are based on real physical parts. Building a physical circuit can be time consuming, but this will deliver the real behavior.
The alternative is to build a model of a component.
Model Circuits#
… behavioral design methods based on a “hardware definition language” such as …
HDL is typically called hardware description language.
Exercise 20
What is the difference between a behavioral and a structural representation?
Solution to Exercise 20
Typically a digital circuit design begins modeling with a CAD program or hardware description language. Some description or coding styles are:
structural: predefined components are instantiated and interconnected, e.g., a power supply in series with a resistor
behavioral: e.g.,: if this signal has a rising edge, then reset the value of this register
dataflow or RTL (register-transfer-language): e.g., multiply the contents of register 0 and 1 and write the result in register 2
Exercise 21
What is the advantage of modeling the circuit using a HDL?
Solution to Exercise 21
We can simulate a circuit using the model, so we can have a faster design cycle.
HDL allows us to describe the behavior of a circuit which is much more understandable for humans. This in turn can be synthesized to a structural description and prototyped on an FPGA.
Vivado Tools and Installation#
We should better install the latest version of the tools.
Seven Segment Display#
The text seems to be written for the Blackboard – do not let it trip you up, this page is mostly about seven-segment displays. For example the section Seven Segment controller FPGA IP is mainly for the Blackboard which focuses on IP development with software control.
Exercise 22
On page 4 of the schematic we see that the seven-segment display anodes are not directly connected to the FPGA, but through transistors. What could be the reason?
Solution to Exercise 22
According to the seven-segment display HOUKEM-2841-BSR datasheet, each LED has a forward voltage of 3.3V and typical current of 20mA. In worst case, all eight cathodes will be active which is above maximum that an FPGA logic pin can supply.
Using a transistor we can reduce the current load on the FPGA pin.
Exercise 23
How much current can an FPGA pin deliver maximum?
Solution to Exercise 23
According to DC Input and Output Levels on the datasheet, LVCMOS33 can drive up to 16mA and LVTTL up to 24mA.
Note that LVTTL supports 3.3V compared to TTL at 5V.
Exercise 24
You want to illuminate all of the seven-segment display LEDs. What should you output on the Boolean Board at the display pins?
A) anode: 0, cathode 0
B) anode: 0, cathode 1
C) anode: 1, cathode 0
D) anode: 1, cathode 1
Solution to Exercise 24
On page 4 of the schematic we see that the seven-segment display anodes are not directly connected to the FPGA, but with PNP transistors in between (refer to their symbol in the schematic). PNP transistors are activated if the FPGA drives a 0. Cathode pins are directly connected to the FPGA. So:
A) anode: 0, cathode 0
Strictly speaking resistors are also in series, but the resistors do not change which voltage level we should drive.
Exercise 25
The seven segment display is controlled in a scanning manner.
What does scanning mean?
What is its advantage?
Solution to Exercise 25
A typical seven segment display has eight LEDs in each digit and four digits. To control each LED individually we would need to reserve 32 logic pins. To save precious logic pins, we can drive the LEDs in a scanning manner like analog televisions:

Requirements#
1. Complete the first tutorial (A First Vivado Project)#
After becoming acquainted with the tool flow and you like to work on the command line, try this command line based flow using Makefiles.
I suggest that you use your favorite code editor instead of Vivado’s own editor and lint your code using a verilator, xvlog, etc and use Vivado only for simulation and synthesis. Especially in the beginning you may do a lot of syntax errors and using linting you get an immediate feedback compared to synthesis in Vivado which may take seconds.
Some examples:
If you like
vim, then installingverilatorshould automatically lint your code when writing.
Finally some useful resources if you want to implement your own makefile or scripts for your own synthesis flow:
2. Complete the second tutorial (Controlling LEDs using Slide Switches)#
In this circuit we want to connect slide switches to the LEDs with the FPGA in between. The FPGA will not contain any logic but only output the input logic level on specified pins.
Basic Input/Output Devices#
Source: Basic Digital I/O: Slide Switch, Push Button and LED
Basic Output Devices: LED#
Exercise 27
How can we determine the voltage drop on an LED?
Solution to Exercise 27
By measuring with a multimeter during operation.
By determining the working condition, e.g., how much current does the LED draw and then referring to its datasheet. If we do not know its part number, we could refer to the datasheet of a random LED with the same color. Different colors tend to have different characteristics.
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)#
Source: Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Protoboards#
Exercise 28
What is the advantage of breadboards, a.k.a., protoboards?
Solution to Exercise 28
As the name protoboards suggests, they are mainly for prototyping circuits. We can easily modify the circuit by dis/connecting components and have a convenient access to the inputs and outputs of individual components, e.g., for measurements.
Printed Circuit Boards#
Exercise 29
Look at the FPGA PCB.
Enumerate major steps from a a schematic to the end product that you have in your hands.
Enumerate the board manufacturing steps from a blank board to the assembled board.
Solution to Exercise 29
The major steps are:

Steps:
Finally the components are soldered to the board. Note that also other manufacturing approaches exist: PCB Construction – Wikipedia
Connectors#
Source: Connectors
Exercise 30
Which connectors do you recognize on the board?
Solution to Exercise 30
USB Micro
HDMI
Pin headers
3.5mm audio jack (compared to 6.5mm on electrical guitars for example)
Integrated Circuits#
Source: Integrated Circuits
Exercise 31
Which integrated circuits are packaged as DIP on the board?
Solution to Exercise 31
All of the chips use surface-mount device (frequently referred as SMD) using surface-mount technology.
The seven-segment LED uses dual inline pins, but it is unlikely a integrated circuit. LEDs with integrated circuits exist though.
Exercise 32
How are tiny integrated circuits wired to the package pins?
Solution to Exercise 32
Using wire bonding:

Note that these contacts where the wire bonds are soldered on are connected to the package pins:

Exercise 33
We see a lot of surface-mounted packages compared to through hole packages. What could be the reason?
Solution to Exercise 33
Surface-mounted packages take less space on the board.
Some components may be available only in a certain package. For example the FPGA packaged as ball-grid-array on the board will be very unlikely available in a DIP package, as it has about 210 input/outputs [2]
A Brief History of Verilog#
Source: A Brief History of Verilog
Exercise 34
According to the text, Verilog and VHDL were created as specification languages for circuits.
What was/is the advantage of specifying a circuit using a specification language?
What did change in the coming decades?
Solution to Exercise 34
Using a standardized language the engineers can communicate their designs in an unambiguous way. Moreover, they can simulate the design before manufacturing. Note that drawing the designs for very large scale integration was probably an individual step.
Synthesizers emerged that could create physical circuits (compare for loops with actual logic gates) from the specification similar to code generation using UML.
A first look at Verilog#
Source: A first look at Verilog
Exercise 35
A module can have inputs and outputs. In the module definition we may see wires. What is the difference between an input and wire?
Solution to Exercise 35
input is implicitly a wire used as input in the module. wire is used to create intermediate signals, similar to variables containing intermediate values in programming.





